3 Wire Rtd Bridge Circuit
Figure 3 shows a typical 3 wire constant current circuit while figure 4 shows a constant voltage excitation circuit.
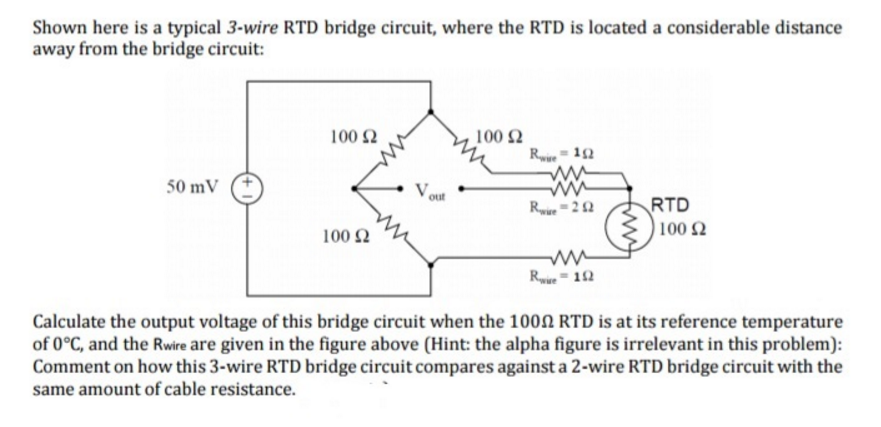
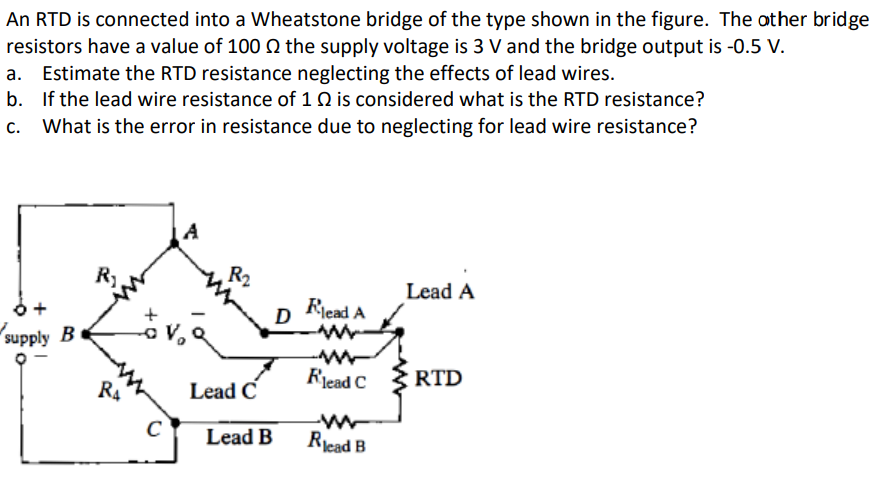
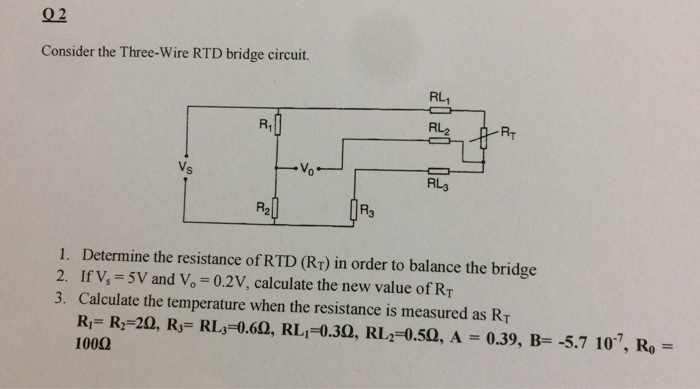
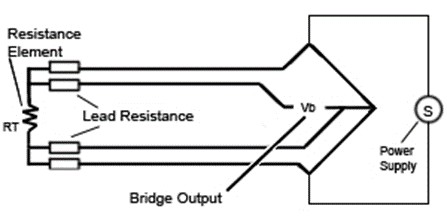
3 wire rtd bridge circuit. The design uses a resistance temperature detector rtd in a 3 wire configuration to minimize the errors introduced by the lead resistances of a remotely located rtd. It consists of running an additional wire to one contact of the rtd. Since l1 and l3 are in separate arms of the bridge resistance is canceled. A 2 wire rtd configuration is the most useful with high resistance sensors or in applications where a great deal of accuracy is not required.
Incidentally the same limitation as for three wire connections applies if the fixed bridge direct reading approach is being used see section 3 3. Tempco matches rtd leads within 5. No current flows through it while the bridge is in balance. The third wire r l3 in figure 3 is a voltage sensing wire only it is not in series with any of the bridge arms therefore it has no effect on bridge balance or temperature stability.
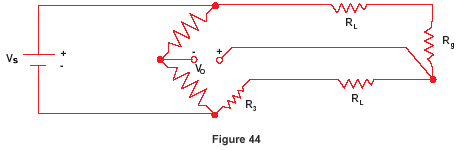
The 3 wire circuit makes it possible to compensate for the line resistance both in its amount and also in its temperature variation. It can be seen that the resistance of the right leg of the wheatstone bridge is r1 r2 rw2. The power supply is connected to one end of the rtd and the top of the wheatstone bridge. This circuit assumes high impedance at eo and close matching of resistance between wires l2 and l3.
While the three wire circuit offers several advantages over the two wire circuit in some special applications involving. A 24 bit delta sigma δσ analog to digital converter adc is used in this design which features two integrated precision current sources that excite the 3 wire rtd. This results in two measuring circuits of which one is used as reference. As a rule of thumb 3 wire circuits can handle wire runs up to 100 feet.
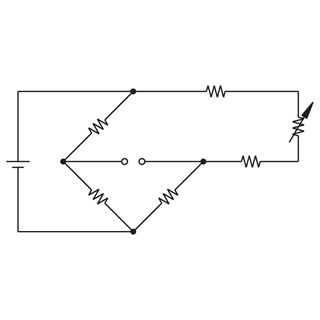
The resistance of the left leg of the bridge is r3 rw3 rtd. Similar to the two wire circuit the current source ik2 is used to measure the temperature dependent resistance rt including the lead and terminal contact resistances. Differential temperature rtd s to measure differential temperatures using bridge circuitry a second rtd is simply introduced into the bridge circuit alongside the first sensor. 3 wire rtd circuit in a three wire circuit two constant current sources are used in order to compensate for the disadvantages described above for the two wire circuits.